Send Arbitrary Data
In this tutorial, you will use Chainlink CCIP to send data between smart contracts on different blockchains. First, you will pay for the CCIP fees on the source blockchain using LINK. Then, you will use the same contract to pay CCIP fees in native gas tokens. For example, you would use ETH on Ethereum or AVAX on Avalanche.
Before you begin
- You should understand how to write, compile, deploy, and fund a smart contract. If you need to brush up on the basics, read this tutorial, which will guide you through using the Solidity programming language, interacting with the MetaMask wallet and working within the Remix Development Environment.
- Your account must have some AVAX tokens on Avalanche Fuji and ETH tokens on Ethereum Sepolia.
- Learn how to Acquire testnet LINK and Fund your contract with LINK.
Tutorial
In this tutorial, you will send a string text between smart contracts on Avalanche Fuji and Ethereum Sepolia using CCIP. First, you will pay CCIP fees in LINK, then you will pay CCIP fees in native gas.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.24;
import {IRouterClient} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/ccip/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";
import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";
import {Client} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/ccip/libraries/Client.sol";
import {CCIPReceiver} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/ccip/applications/CCIPReceiver.sol";
import {IERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
import {SafeERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";
/**
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY.
* THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE.
* DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION.
*/
/// @title - A simple messenger contract for sending/receving string data across chains.
contract Messenger is CCIPReceiver, OwnerIsCreator {
using SafeERC20 for IERC20;
// Custom errors to provide more descriptive revert messages.
error NotEnoughBalance(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); // Used to make sure contract has enough balance.
error NothingToWithdraw(); // Used when trying to withdraw Ether but there's nothing to withdraw.
error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); // Used when the withdrawal of Ether fails.
error DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 destinationChainSelector); // Used when the destination chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner.
error SourceChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 sourceChainSelector); // Used when the source chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner.
error SenderNotAllowlisted(address sender); // Used when the sender has not been allowlisted by the contract owner.
error InvalidReceiverAddress(); // Used when the receiver address is 0.
// Event emitted when a message is sent to another chain.
event MessageSent(
bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message.
uint64 indexed destinationChainSelector, // The chain selector of the destination chain.
address receiver, // The address of the receiver on the destination chain.
string text, // The text being sent.
address feeToken, // the token address used to pay CCIP fees.
uint256 fees // The fees paid for sending the CCIP message.
);
// Event emitted when a message is received from another chain.
event MessageReceived(
bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message.
uint64 indexed sourceChainSelector, // The chain selector of the source chain.
address sender, // The address of the sender from the source chain.
string text // The text that was received.
);
bytes32 private s_lastReceivedMessageId; // Store the last received messageId.
string private s_lastReceivedText; // Store the last received text.
// Mapping to keep track of allowlisted destination chains.
mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedDestinationChains;
// Mapping to keep track of allowlisted source chains.
mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedSourceChains;
// Mapping to keep track of allowlisted senders.
mapping(address => bool) public allowlistedSenders;
IERC20 private s_linkToken;
/// @notice Constructor initializes the contract with the router address.
/// @param _router The address of the router contract.
/// @param _link The address of the link contract.
constructor(address _router, address _link) CCIPReceiver(_router) {
s_linkToken = IERC20(_link);
}
/// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given destinationChainSelector is allowlisted.
/// @param _destinationChainSelector The selector of the destination chain.
modifier onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(uint64 _destinationChainSelector) {
if (!allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector])
revert DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(_destinationChainSelector);
_;
}
/// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given sourceChainSelector is allowlisted and if the sender is allowlisted.
/// @param _sourceChainSelector The selector of the destination chain.
/// @param _sender The address of the sender.
modifier onlyAllowlisted(uint64 _sourceChainSelector, address _sender) {
if (!allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector])
revert SourceChainNotAllowlisted(_sourceChainSelector);
if (!allowlistedSenders[_sender]) revert SenderNotAllowlisted(_sender);
_;
}
/// @dev Modifier that checks the receiver address is not 0.
/// @param _receiver The receiver address.
modifier validateReceiver(address _receiver) {
if (_receiver == address(0)) revert InvalidReceiverAddress();
_;
}
/// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a destination chain for transactions.
function allowlistDestinationChain(
uint64 _destinationChainSelector,
bool allowed
) external onlyOwner {
allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector] = allowed;
}
/// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a source chain for transactions.
function allowlistSourceChain(
uint64 _sourceChainSelector,
bool allowed
) external onlyOwner {
allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector] = allowed;
}
/// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a sender for transactions.
function allowlistSender(address _sender, bool allowed) external onlyOwner {
allowlistedSenders[_sender] = allowed;
}
/// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain.
/// @notice Pay for fees in LINK.
/// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient LINK.
/// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain.
/// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain.
/// @param _text The text to be sent.
/// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent.
function sendMessagePayLINK(
uint64 _destinationChainSelector,
address _receiver,
string calldata _text
)
external
onlyOwner
onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector)
validateReceiver(_receiver)
returns (bytes32 messageId)
{
// Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message
Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage(
_receiver,
_text,
address(s_linkToken)
);
// Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router
IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter());
// Get the fee required to send the CCIP message
uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage);
if (fees > s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)))
revert NotEnoughBalance(s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees);
// approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK
s_linkToken.approve(address(router), fees);
// Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID
messageId = router.ccipSend(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage);
// Emit an event with message details
emit MessageSent(
messageId,
_destinationChainSelector,
_receiver,
_text,
address(s_linkToken),
fees
);
// Return the CCIP message ID
return messageId;
}
/// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain.
/// @notice Pay for fees in native gas.
/// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient native gas tokens.
/// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain.
/// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain.
/// @param _text The text to be sent.
/// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent.
function sendMessagePayNative(
uint64 _destinationChainSelector,
address _receiver,
string calldata _text
)
external
onlyOwner
onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector)
validateReceiver(_receiver)
returns (bytes32 messageId)
{
// Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message
Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage(
_receiver,
_text,
address(0)
);
// Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router
IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter());
// Get the fee required to send the CCIP message
uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage);
if (fees > address(this).balance)
revert NotEnoughBalance(address(this).balance, fees);
// Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID
messageId = router.ccipSend{value: fees}(
_destinationChainSelector,
evm2AnyMessage
);
// Emit an event with message details
emit MessageSent(
messageId,
_destinationChainSelector,
_receiver,
_text,
address(0),
fees
);
// Return the CCIP message ID
return messageId;
}
/// handle a received message
function _ccipReceive(
Client.Any2EVMMessage memory any2EvmMessage
)
internal
override
onlyAllowlisted(
any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector,
abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address))
) // Make sure source chain and sender are allowlisted
{
s_lastReceivedMessageId = any2EvmMessage.messageId; // fetch the messageId
s_lastReceivedText = abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)); // abi-decoding of the sent text
emit MessageReceived(
any2EvmMessage.messageId,
any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, // fetch the source chain identifier (aka selector)
abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)), // abi-decoding of the sender address,
abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string))
);
}
/// @notice Construct a CCIP message.
/// @dev This function will create an EVM2AnyMessage struct with all the necessary information for sending a text.
/// @param _receiver The address of the receiver.
/// @param _text The string data to be sent.
/// @param _feeTokenAddress The address of the token used for fees. Set address(0) for native gas.
/// @return Client.EVM2AnyMessage Returns an EVM2AnyMessage struct which contains information for sending a CCIP message.
function _buildCCIPMessage(
address _receiver,
string calldata _text,
address _feeTokenAddress
) private pure returns (Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory) {
// Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message
return
Client.EVM2AnyMessage({
receiver: abi.encode(_receiver), // ABI-encoded receiver address
data: abi.encode(_text), // ABI-encoded string
tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), // Empty array as no tokens are transferred
extraArgs: Client._argsToBytes(
// Additional arguments, setting gas limit
Client.EVMExtraArgsV2({
gasLimit: 200_000, // Gas limit for the callback on the destination chain
allowOutOfOrderExecution: true // Allows the message to be executed out of order relative to other messages from the same sender
})
),
// Set the feeToken to a feeTokenAddress, indicating specific asset will be used for fees
feeToken: _feeTokenAddress
});
}
/// @notice Fetches the details of the last received message.
/// @return messageId The ID of the last received message.
/// @return text The last received text.
function getLastReceivedMessageDetails()
external
view
returns (bytes32 messageId, string memory text)
{
return (s_lastReceivedMessageId, s_lastReceivedText);
}
/// @notice Fallback function to allow the contract to receive Ether.
/// @dev This function has no function body, making it a default function for receiving Ether.
/// It is automatically called when Ether is sent to the contract without any data.
receive() external payable {}
/// @notice Allows the contract owner to withdraw the entire balance of Ether from the contract.
/// @dev This function reverts if there are no funds to withdraw or if the transfer fails.
/// It should only be callable by the owner of the contract.
/// @param _beneficiary The address to which the Ether should be sent.
function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner {
// Retrieve the balance of this contract
uint256 amount = address(this).balance;
// Revert if there is nothing to withdraw
if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw();
// Attempt to send the funds, capturing the success status and discarding any return data
(bool sent, ) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}("");
// Revert if the send failed, with information about the attempted transfer
if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount);
}
/// @notice Allows the owner of the contract to withdraw all tokens of a specific ERC20 token.
/// @dev This function reverts with a 'NothingToWithdraw' error if there are no tokens to withdraw.
/// @param _beneficiary The address to which the tokens will be sent.
/// @param _token The contract address of the ERC20 token to be withdrawn.
function withdrawToken(
address _beneficiary,
address _token
) public onlyOwner {
// Retrieve the balance of this contract
uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this));
// Revert if there is nothing to withdraw
if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw();
IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount);
}
}
Deploy your contracts
To use this contract:
-
Compile your contract.
-
Deploy your sender contract on Avalanche Fuji and enable sending messages to Ethereum Sepolia:
- Open MetaMask and select the network Avalanche Fuji.
- In Remix IDE, click on Deploy & Run Transactions and select Injected Provider - MetaMask from the environment list. Remix will then interact with your MetaMask wallet to communicate with Avalanche Fuji.
- Fill in the router address and the link address for your network. You can find the router address on the supported networks page and the LINK token address on the LINK Token contracts page. For Avalanche Fuji:
- The router address is
0xF694E193200268f9a4868e4Aa017A0118C9a8177, - The LINK contract address is
0x0b9d5D9136855f6FEc3c0993feE6E9CE8a297846.
- The router address is
- Click on transact. After you confirm the transaction, the contract address appears on the Deployed Contracts list. Note your contract address.
- Enable your contract to send CCIP messages to Ethereum Sepolia:
- In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Avalanche Fuji.
- Call the
allowlistDestinationChainwith16015286601757825753as the destination chain selector, andtrueas allowed. Each chain selector is found on the supported networks page.
-
Deploy your receiver contract on Ethereum Sepolia and enable receiving messages from your sender contract:
- Open MetaMask and select the network Ethereum Sepolia.
- In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, make sure the environment is still Injected Provider - MetaMask.
- Fill in the router address and the LINK address for your network. You can find the router address on the supported networks page and the LINK contract address on the LINK token contracts page. For Ethereum Sepolia:
- The router address is
0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59, - The LINK contract address is
0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789.
- The router address is
- Click on transact. After you confirm the transaction, the contract address appears on the Deployed Contracts list. Note your contract address.
- Enable your contract to receive CCIP messages from Avalanche Fuji:
- In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Ethereum Sepolia.
- Call the
allowlistSourceChainwith14767482510784806043as the source chain selector, andtrueas allowed. Each chain selector is found on the supported networks page.
- Enable your contract to receive CCIP messages from the contract that you deployed on Avalanche Fuji:
- In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Ethereum Sepolia.
- Call the
allowlistSenderwith the contract address of the contract that you deployed on Avalanche Fuji, andtrueas allowed.
At this point, you have one sender contract on Avalanche Fuji and one receiver contract on Ethereum Sepolia. As security measures, you enabled the sender contract to send CCIP messages to Ethereum Sepolia and the receiver contract to receive CCIP messages from the sender and Avalanche Fuji. Note: Another security measure enforces that only the router can call the _ccipReceive function. Read the explanation section for more details.
Send data and pay in LINK
You will use CCIP to send a text. The CCIP fees for using CCIP will be paid in LINK. Read this explanation for a detailed description of the code example.
-
Open MetaMask and connect to Avalanche Fuji. Fund your contract with LINK tokens. You can transfer
70LINK to your contract. In this example, LINK is used to pay the CCIP fees. -
Send "Hello World!" from Avalanche Fuji:
-
Open MetaMask and select the network Avalanche Fuji.
-
In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Avalanche Fuji.
-
Fill in the arguments of the sendMessagePayLINK function:
Argument Description Value (Ethereum Sepolia) _destinationChainSelector CCIP Chain identifier of the target blockchain. You can find each network's chain selector on the supported networks page 16015286601757825753_receiver The destination smart contract address Your deployed receiver contract address _text any stringHello World! -
Click on
transactand confirm the transaction on MetaMask. -
Once the transaction is successful, note the transaction hash. Here is an example of a transaction on Avalanche Fuji.
-
-
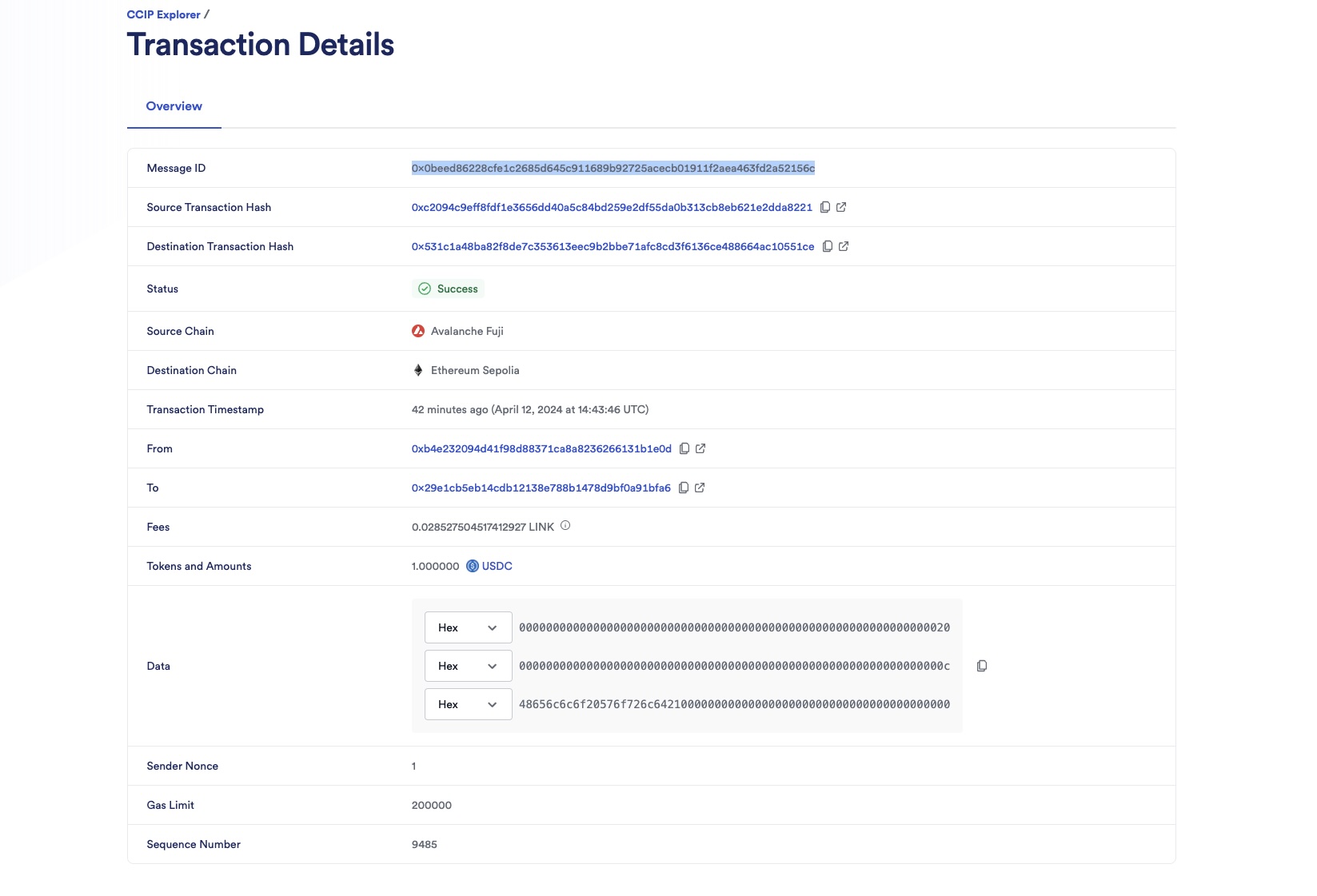
Open the CCIP explorer and search your cross-chain transaction using the transaction hash.
-
The CCIP transaction is completed once the status is marked as "Success". Note: In this example, the CCIP message ID is 0x28a804fa891bde8fb4f6617931187e1033a128c014aa76465911613588bc306f.
-
Check the receiver contract on the destination chain:
-
Open MetaMask and select the network Ethereum Sepolia.
-
In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Ethereum Sepolia.
-
Call the
getLastReceivedMessageDetails.
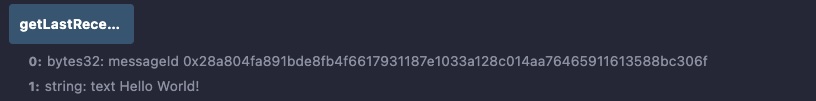
-
Notice the received text is the one you sent, "Hello World!" and the message ID is the one you expect 0x28a804fa891bde8fb4f6617931187e1033a128c014aa76465911613588bc306f.
-
Note: These example contracts are designed to work bi-directionally. As an exercise, you can use them to send data from Avalanche Fuji to Ethereum Sepolia and from Ethereum Sepolia back to Avalanche Fuji.
Send data and pay in native
You will use CCIP to send a text. The CCIP fees for using CCIP will be paid in native gas. Read this explanation for a detailed description of the code example.
-
Open MetaMask and connect to Avalanche Fuji. Fund your contract with AVAX. You can transfer
1AVAX to your contract. In this example, AVAX is used to pay the CCIP fees. -
Send "Hello World!" from Avalanche Fuji:
-
Open MetaMask and select the network Avalanche Fuji.
-
In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Avalanche Fuji.
-
Fill in the arguments of the sendMessagePayNative function:
Argument Description Value (Ethereum Sepolia) _destinationChainSelector CCIP Chain identifier of the target blockchain. You can find each network's chain selector on the supported networks page 16015286601757825753_receiver The destination smart contract address Your deployed receiver contract address _text any stringHello World! -
Click on
transactand confirm the transaction on MetaMask. -
Once the transaction is successful, note the transaction hash. Here is an example of a transaction on Avalanche Fuji.
-
-
Open the CCIP explorer and search your cross-chain transaction using the transaction hash.
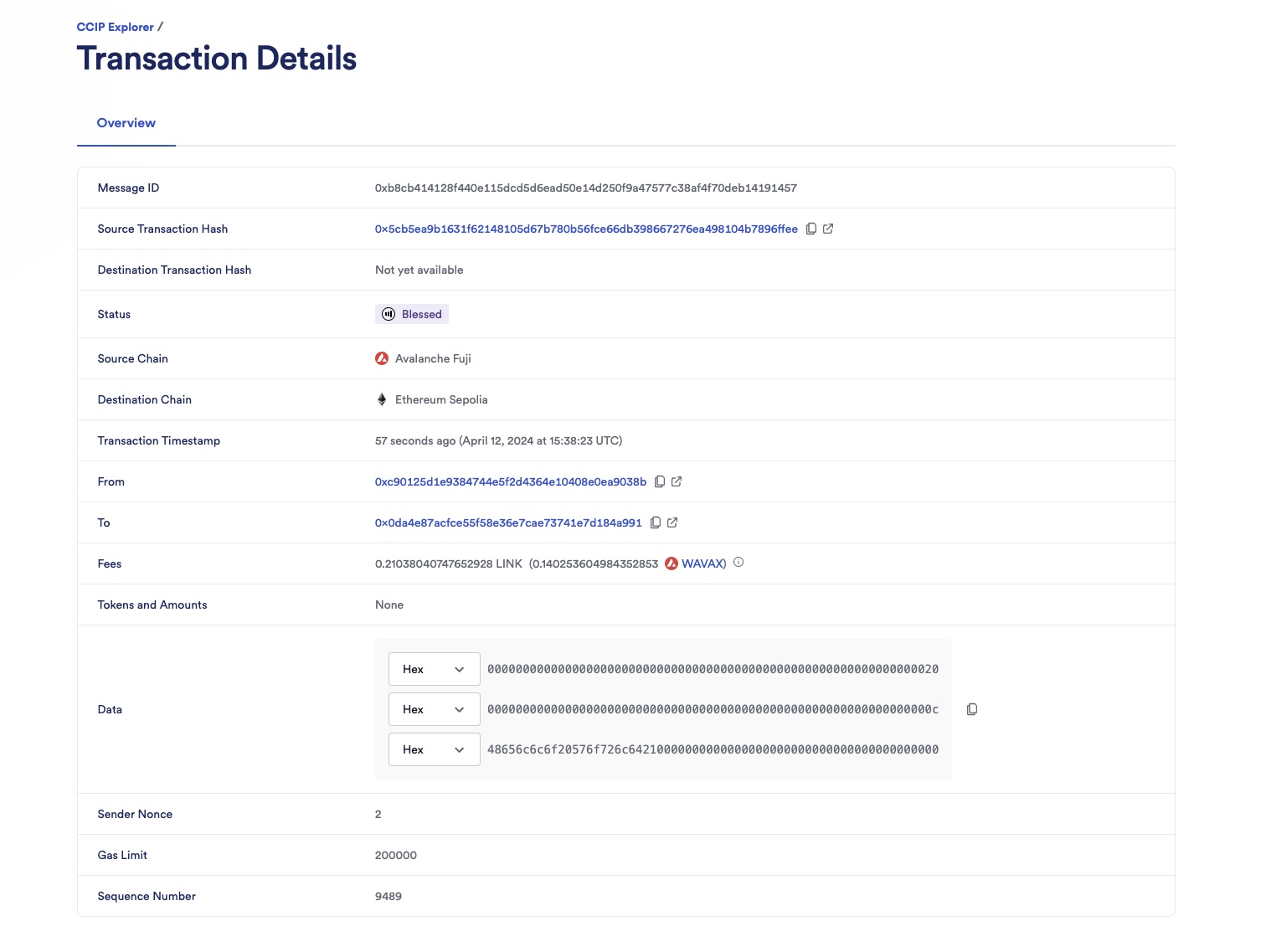
-
The CCIP transaction is completed once the status is marked as "Success". In this example, the CCIP message ID is 0xb8cb414128f440e115dcd5d6ead50e14d250f9a47577c38af4f70deb14191457. Note that CCIP fees are denominated in LINK. Even if CCIP fees are paid using native gas tokens, node operators will be paid in LINK.
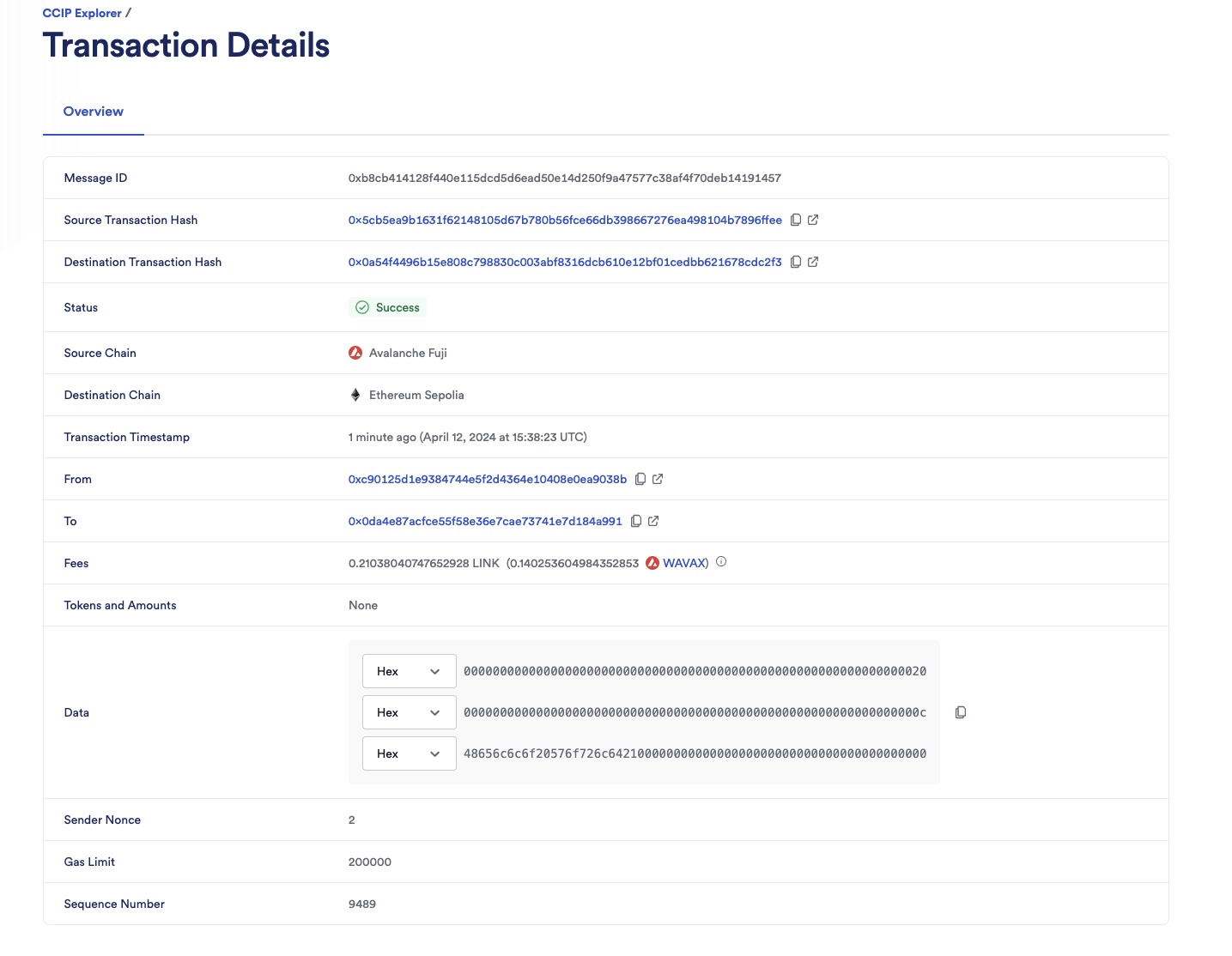
-
Check the receiver contract on the destination chain:
-
Open MetaMask and select the network Ethereum Sepolia.
-
In Remix IDE, under Deploy & Run Transactions, open the list of transactions of your smart contract deployed on Ethereum Sepolia.
-
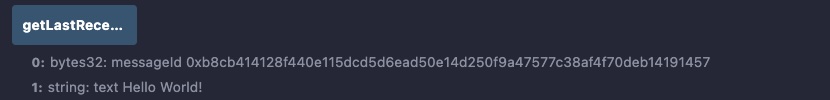
Call the
getLastReceivedMessageDetails.
-
Notice the received text is the one you sent, "Hello World!" and the message ID is the one you expect 0xb8cb414128f440e115dcd5d6ead50e14d250f9a47577c38af4f70deb14191457.
-
Note: These example contracts are designed to work bi-directionally. As an exercise, you can use them to send data from Avalanche Fuji to Ethereum Sepolia and from Ethereum Sepolia back to Avalanche Fuji.
Explanation
The smart contract featured in this tutorial is designed to interact with CCIP to send and receive messages. The contract code contains supporting comments clarifying the functions, events, and underlying logic. Here we will further explain initializing the contract and sending and receiving data.
Initializing of the contract
When deploying the contract, we define the router address and LINK contract address of the blockchain we deploy the contract on. Defining the router address is useful for the following:
-
Sender part:
-
Receiver part:
- The contract inherits from CCIPReceiver, which serves as a base contract for receiver contracts. This contract requires that child contracts implement the
_ccipReceivefunction._ccipReceiveis called by theccipReceivefunction, which ensures that only the router can deliver CCIP messages to the receiver contract.
- The contract inherits from CCIPReceiver, which serves as a base contract for receiver contracts. This contract requires that child contracts implement the
Sending data and pay in LINK
The sendMessagePayLINK function undertakes five primary operations:
-
Call the
_buildCCIPMessageprivate function to construct a CCIP-compatible message using theEVM2AnyMessagestruct:-
The
_receiveraddress is encoded in bytes to accommodate non-EVM destination blockchains with distinct address formats. The encoding is achieved through abi.encode. -
The
datais encoded from astringtobytesusing abi.encode. -
The
tokenAmountsis an emptyEVMTokenAmountstruct array as no tokens are transferred. -
The
extraArgsspecifies thegasLimitfor relaying the message to the recipient contract on the destination blockchain. In this example, thegasLimitis set to200000. -
The
_feeTokenAddressdesignates the token address used for CCIP fees. Here,address(linkToken)signifies payment in LINK.
-
-
Computes the fees by invoking the router's
getFeefunction. -
Ensures your contract balance in LINK is enough to cover the fees.
-
Grants the router contract permission to deduct the fees from the contract's LINK balance.
-
Dispatches the CCIP message to the destination chain by executing the router's
ccipSendfunction.
Note: As a security measure, the sendMessagePayLINK function is protected by the onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain, ensuring the contract owner has allowlisted a destination chain.
Sending data and pay in native
The sendMessagePayNative function undertakes four primary operations:
-
Call the
_buildCCIPMessageprivate function to construct a CCIP-compatible message using theEVM2AnyMessagestruct:-
The
_receiveraddress is encoded in bytes to accommodate non-EVM destination blockchains with distinct address formats. The encoding is achieved through abi.encode. -
The
datais encoded from astringtobytesusing abi.encode. -
The
tokenAmountsis an emptyEVMTokenAmountstruct array as no tokens are transferred. -
The
extraArgsspecifies thegasLimitfor relaying the message to the recipient contract on the destination blockchain. In this example, thegasLimitis set to200000. -
The
_feeTokenAddressdesignates the token address used for CCIP fees. Here,address(0)signifies payment in native gas tokens (ETH).
-
-
Computes the fees by invoking the router's
getFeefunction. -
Ensures your contract balance in native gas is enough to cover the fees.
-
Dispatches the CCIP message to the destination chain by executing the router's
ccipSendfunction. Note:msg.valueis set because you pay in native gas.
Note: As a security measure, the sendMessagePayNative function is protected by the onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain, ensuring the contract owner has allowlisted a destination chain.
Receiving data
On the destination blockchain, the router invokes the ccipReceive function which expects an Any2EVMMessage struct that contains:
- The CCIP
messageId. - The
sourceChainSelector. - The
senderaddress in bytes format. Given that the sender is known to be a contract deployed on an EVM-compatible blockchain, the address is decoded from bytes to an Ethereum address using the ABI specifications. - The
data, which is also in bytes format. Given astringis expected, the data is decoded from bytes to a string using the ABI specifications.
This example applies three important security measures: